Name
________________________________________________ Period _________________
Exam:
Ionic Bonding
50 points total. Each problem is worth 1 point.
1. An atom that
has gained or lost an electron is called
a. a proton.
b. a neutron.
c. a positron.
d. an ion.
e. a neutral
ion.
2. A positively
charged ion is called
a. a cation.
b. an anion.
c. an electron.
d. a proton.
e. a neutron.
3. Electrons in
the outer shell are called
a. external
electrons.
b. valance electrons.
c. neutrons.
d. cations.
e. anions.
4. A helium
atom contains
a. 0 protons.
b. one proton.
c. two protons.
d. usually two,
but sometimes 3 protons.
e. 3 protons.
5. This atom
has 79 protons.
a. hydrogen.
b. helium.
c. lead.
d. silver.
e. gold.
6. This atom
has 47 electrons.
a. hydrogen.
b. helium.
c. lead.
d. silver.
e. gold.
7. 78% of the
air we breathe is composed of this gas that has 7 protons.
a. oxygen
b. nitrogen
c. carbon
dioxide
d. carbon
monoxide
e. helium
8. Neon has 10
protons. How many of these protons are
contained in its nucleus?
a. 0
b. 2
c. 5
d. 8
e. 10
9. This noble
gas has 2 electrons
a. hydrogen
b. helium
c. neon
d. argon
e. lithium
10. The
second most abundant element in the Earth’s crust has 14 neutrons. It is
a. carbon.
b. iron.
c. soil.
d. aluminum.
e. gold.
11. What
causes the Northern Lights?
a. the Aurora Australis
b. charged particles (ions) from the Sun
interacting with Earth’s magnetic field.
c. baking soda
and vinegar
d. the moon
e. supernovae
12. How many
electrons can the first shell of an atom contain before it is full?
a. 1
b. 2
c. 4
d. 8
e. there is no
limit
13. An atom
has a neutral charge because
a. of neutrons.
b. it has more
protons than electrons.
c. it has more
electrons than protons.
d. it has an
equal number of protons and neutrons.
e. it has an equal number of protons and
electrons.
14. A proton
a. is more massive than an electron.
b. is less
massive than an electron.
c. has the same
mass as an electron.
d. can only
exist in a shell around the nucleus.
e. has a
negative charge.
Show the transfer of
electrons in the following combinations:
Example: Na +
O Na +
O + Na ![]()
15. Na + Cl
16. K + F
17. Be + S
18. Ca + Cl
19. Mg + I
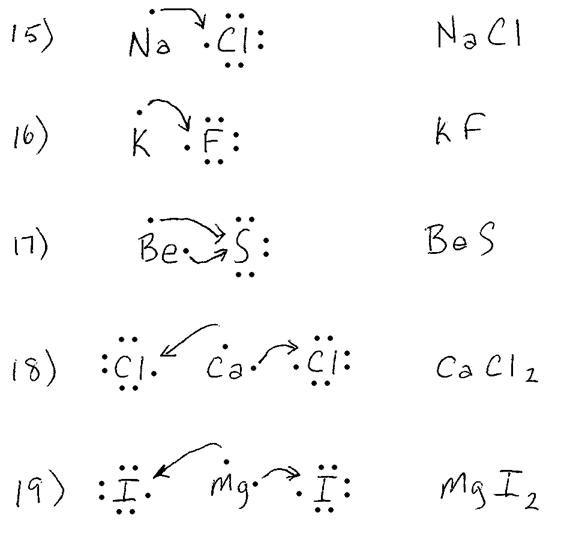
Use the criss-cross method to write the formulas of
the compounds produced from the following ions.
Example: ![]()
20. ![]()
![]()
21. ![]()
![]()
22. ![]()
![]()
23. Potassium and Chlorine (hint:
compute the charge from the valence electrons) ![]()
24. Aluminum and Chlorine (hint:
compute the charge from the valence electrons)
![]()
Write the formulas of the
following compounds.
25. iron(II) oxide ![]()
26. potassium nitrate ![]()
27. ammonium phosphate ![]()
28. copper (II) sulfate ![]()
29. zinc nitrate ![]()
Name the following compounds.
30. ![]() iron(III) oxide 31.
iron(III) oxide 31. ![]() calcium carbonate
calcium carbonate
32. ![]() *** mercury(I) chloride *** 33.
*** mercury(I) chloride *** 33. ![]() *** lead
(II) sulfite ***
*** lead
(II) sulfite ***
34. ![]() copper(II) sulfate
copper(II) sulfate
Name the following ions.
35. ![]() silver 36.
silver 36. ![]() sodium
sodium
37. ![]() Nickel(II) 38.
Nickel(II) 38. ![]() sulfide
sulfide
39. ![]() Floride
Floride
40. ![]() mercury(II) or mercuric 41.
mercury(II) or mercuric 41. ![]() lead
lead
42. ![]() carbonate 43.
carbonate 43. ![]() nitrite
nitrite
44. ![]() iodide
iodide
45 – 50. Complete the following table.
|
Name |
Symbol |
Atomic number |
Number of protons |
Number of electrons |
Number of neutrons |
Electron arrangement |
|
Hydrogen |
H |
1 |
1 |
1 |
0 |
1 |
|
Helium |
He |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
2 |
|
Nitrogen |
N |
7 |
7 |
7 |
7 |
2,5 |
|
Oxygen |
O |
8 |
8 |
8 |
8 |
2,6 |
|
Aluminum |
Al |
13 |
13 |
13 |
14 |
2,8,3 |
|
Chlorine |
Cl |
17 |
17 |
17 |
18 |
2,8,7 |