|
Semi-Major Axis Calculator
An object's semi-major axis can be computed from its orbital period and the mass of the body it orbits using the following formula:
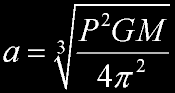
|
- a is the semi-major axis of the object
- P is the orbital period
- G is the gravitational constant
- M is the combined mass of primary and secondary bodies. The mass of the secondary body may be ignored when it is insignificant compared to the mass of the primary, as is the case for a spacecraft orbiting a planet.
|
Sample problems:
1. Mission Control wishes to place a satellite in circular orbit above the Earth. The satellite must have a period of 12 hours. How many miles above the surface of the Earth will this satellite orbit?
Enter 12 h for P and 1 M_Earth for M and 1R_Earth for r.
Choose mi for the answer's units. The calculator gives you an answer of 12576 mi.
Change the output units from s to h. It now gives you an answer of 1.6195 hr.
|
2. Astronomers discover a distant planet orbiting the Sun. It's semi-major axis is 1 light year. What is the planet's orbital period in years?
Enter 1 LY for a and 1 Ms for M.
The calculator gives you an answer of 501850205474964.06 s.
Change the output units from s to yr. It now gives you an answer of 15902421.421915896 yr.
|
Formulas on this page were generated with Math Type.
| |

