Name____________________________________________ Period
_______________
Electromagnetic wave worksheet
On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions. Staple your answers to this sheet.
1. What kind of wave
is a light wave?
A light
wave is a transverse wave. It is also an
electromagnetic wave.
2. What is a
medium? Give some examples.
A medium
is a substance that longitudinal waves (also known as compressional waves)
travel through. The longitudinal wave
compresses and rarifies the medium as the wave transfers energy from one place
to another.
Some
examples of mediums are air, water, wood and metal. When I speak to you, my voice creates sound
waves by compressing and rarifying the air.
This sound wave carries energy to your eardrum. The compressions and rarifications cause your
eardrum to vibrate at the same pattern as the vibrations that left my vocal
cords. That is how you hear what I say. This is easier to understand if you look at
the cone of a speaker. You can watch it
vibrate, and imagine the compressions in creates in the air.
3. What is a vacuum?
A vacuum
is a lack of a medium. A vacuum is
“nothingness”. Space is a vacuum. There is no air on the Moon, so if you were
standing on the Moon, you would be in a vacuum.
4. Can sound travel
through a vacuum?
No. Sound is a longitudinal wave (also known as a
compressional wave). It needs a medium
to compress and rarify in order for the wave to carry energy from one place to
another. Although we can see the Sun, we can not hear the Sun. That is because a vacuum exists in between
Earth and the Sun. If sound could
travel through a vacuum, the Sun would be deafeningly loud. We are lucky sound doesn’t travel through
vacuums.
5. Can light travel
through a vacuum?
Yes. We know this because we can see the Sun, and
other objects in space.
6. Is light the only
electromagnetic wave? If not, give some
other examples.
No. Other electromagnetic waves include radio
waves, infrared waves, ultraviolet waves, microwaves, x-rays and gamma rays.
7. What is the
wavelength range for the FM radio band (88 MHz – 108 MHz)?
(Don’t
let the lengthiness of my response scare you.
I’m just spelling it out in great detail. The actual solution I expect on a test is
only about 2 lines long.)
Wavelength
is a distance. It is the distance
between a point on a wave, and the next identical point on a wave. Hz is a frequency. It means 1/second. Frequency is the inverse of period, which is
the amount of time it takes a wave to move one wavelength. M means “mega”, which means million. So replace mega with ![]() .
.
To solve
this problem, start with the formula you are already familiar with:
![]()
Before
you even set foot in a Physics class, you knew this formula. I’ve reminded you many times in class by
asking you “If you travel at 60 miles per hour for 2 hours, how far have you
gone?” All of you confidently answer
“120 miles”, which is what you get if you multiply your velocity by your time,
demonstrating that you already knew this formula.
Since
wavelength is a distance, we can replace it with the Greek letter Lambda, λ, which is the variable we use to
represent wavelength. And since time =
1/frequency, we can replace t with 1/f.
Since the velocity of any electromagnetic wave is the speed of light,
and we use the letter c to represent
the speed of light, we can replace v
with c. Remember, ![]() . Then we are ready to
solve for wavelength with the data from the question.
. Then we are ready to
solve for wavelength with the data from the question.
For 88 MHz
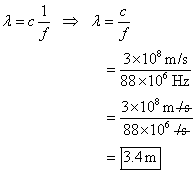
And for
108 MHz
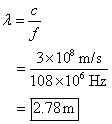
So the
wavelength range for the FM radio band is 2.78 m to 3.4 m.
8. What is the
frequency of an electromagnetic wave if it has a wavelength of 1.0 km? In what part of the electromagnetic spectrum
is this wave? (Refer
to p. 387 of Hewitt).
(
In the
following solution, I again start out with the formula we are all familiar
with, d=vt, and modify it to fit this problem. But you could always start with f=v/d if you want, to make your solution
simpler.)
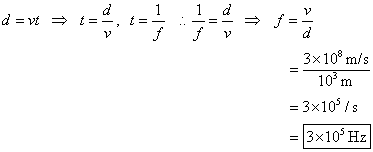
Looking
at p. 387 of Hewitt, I can see that this is a radio wave.
9. Shortwave radio
is broadcast between 3.50 and 29.7 MHz.
To what range of wavelengths does this correspond? Why do you suppose this part of the spectrum
is called shortwave radio?
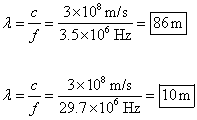
So the
rage of wavelengths is 10 m to 86 m.
Since
radio waves can be as long as 1000 km, these are pretty short for radio
waves. That’s why they call them
shortwave radio.
10. A burst is a brief
flash or pulse of light or other electromagnetic wave. Gamma-ray bursters
are objects in the universe that emit pulses of gamma rays with high
energies. The frequency of the most
energetic bursts has been measured at around ![]() . What is the
wavelength of these gamma rays?
. What is the
wavelength of these gamma rays?
![]()
11. The portion of the
visible spectrum that appears brightest to the human eye is around 500 nm in wavelength, which corresponds to yellow-green. What is the frequency of 560 nm light?
![]()
12. What is the
frequency of highly energetic ultraviolet radiation that has a wavelength of
125 nm?
![]()