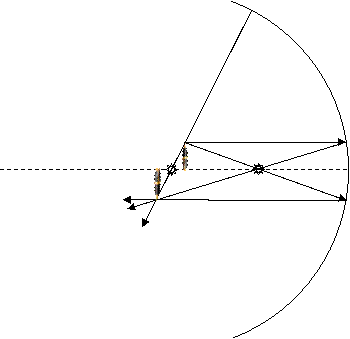Name__________________________________________ Period ______________
Concave Mirror Worksheet
On a separate sheet of paper, answer the following questions.
1. A concave makeup mirror is designed so that a person 25.0 cm in front of it sees an upright image at a distance of 50.0 cm behind the mirror.
a. What is the radius of curvature of the mirror.
Begin with the mirror equation on p. 532 of Holt.
![]()
where
· p is the distance of the object to the surface of the mirror
· q is the distance of the image to the surface of the mirror
· f is the distance from the focal point to the image
The radius of curvature, R, is twice the focal length. So we can modify the mirror equation and use the equation on p. 531 of Holt to solve for the radius
![]()
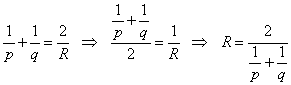
Plug in and solve
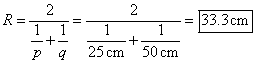
b. What is the magnification of the image?
The equation for magnification is given on p. 533 of Holt.
![]()
c. Is the image real or virtual?
The light rays converge on the image location, so the image is real.
2. A concave shaving mirror has a focal length of 33 cm.
a. Calculate the image position of a razor placed in front of the mirror at a distance of 93 cm.
Use algebra to rewrite the mirror equation on p. 532 of Holt to solve for the image position, q.
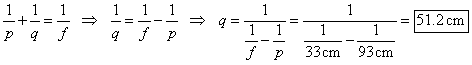
· p is the distance of the object to the surface of the mirror
· q is the distance of the image to the surface of the mirror
· f is the distance from the focal point
b. Calculate the magnification of the image.
The equation for magnification is given on p. 533 of Holt.
![]()
c. Is the image real or virtual?
The light rays converge on the image location, so the image is real.
d. Draw a ray diagram to show where the image forms and how large it is with respect to the object.
Use the table on p. 14-3 to create the ray diagram.

R f
3. A pen placed 11.0 cm from a concave spherical mirror produces a real image 13.2 cm from the mirror.
a. What is the focal length of the mirror?
Use algebra to rewrite the mirror equation on p. 532 of Holt to solve for the focal length.
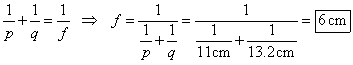
· p is the distance of the object to the surface of the mirror
· q is the distance of the image to the surface of the mirror
· f is the distance from the focal point
b. What is the magnification of the image?
The equation for magnification is given on p. 533 of Holt.
![]()
c. If the pen is placed 27.0 cm from the mirror, what is the new position of the image?
Use algebra to rewrite the mirror equation on p. 532 of Holt to solve for the image position.
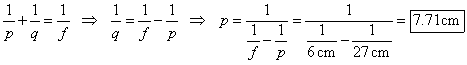
d. What is the magnification of the new image?
The equation for magnification is given on p. 533 of Holt.
![]()
e. Is the new image real or virtual?
It is a real image since the rays converge.
f. Draw ray diagrams to confirm your results.
Yes, the first ray diagram, when the pen was 11 cm from the mirror shows an inverted image that is slightly larger than the object, agreeing with our computed magnification of –1.2.
The second ray diagram, when the pen was 27 cm in front of the mirror shows an inverted image that is much smaller than the object, agreeing with our computed magnification of –0.286.